STORAGE COEFFICIENT
The water yielding capacity of a confined aquifer can be expressed in terms of
its storage coefficient. Storage coefficient is defined as the volume of water
that an aquifer releases from or takes into storage per unit surface area of
aquifer per unit change in the component of head normal to that surface.
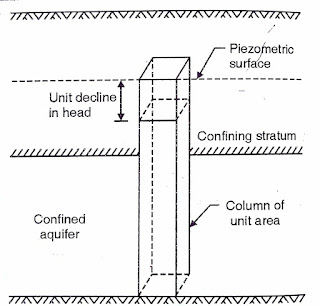
Let us consider a vertical column of unit area (one metre x
one metre) extending through a confined aquifer. Then, the storage coefficient,
S is the volume of water, in cubic metres, released from the aquifer when the
piezometric surface declines by one metre. In most of the confined aquifers,
the value of storage co-efficient ranges between 0.00005 to 0.005. Its value
can be determined from pumping out tests on wells penetrating fully into
confined aquifer.
In an unconfined aquifer, when the water table is lowered by
one metre, the water from one metre height of the vertical column of unit area
drains freely under gravity. Thus, storage coefficient for an unconfined
aquifer corresponds to its specific yield.
Coefficient of
Permeability (h):
The coefficient of permeability is defined as the velocity
of flow which will occur through the total cross-sectional area of the soil (or
aquifer) under a unit hydraulic gradient.
Coefficient of
Transmissibility (T):
Coefficient of transmissibility is defined as the rate
of flow of water (in m³/day or gallons/day) through vertical strip of aquifer
of unit width (1 m or 1 ft) and extending the full saturation height under unit
hydraulic gradient, at a temperature of 60° F. Thus, the coefficient of
transmissibility T equals to the field coefficient of permeability multiplied
by the aquifer thickness (B) :
T = B k.
No comments:
Post a Comment